VMDL: Volcano Monitoring using Deep Learning
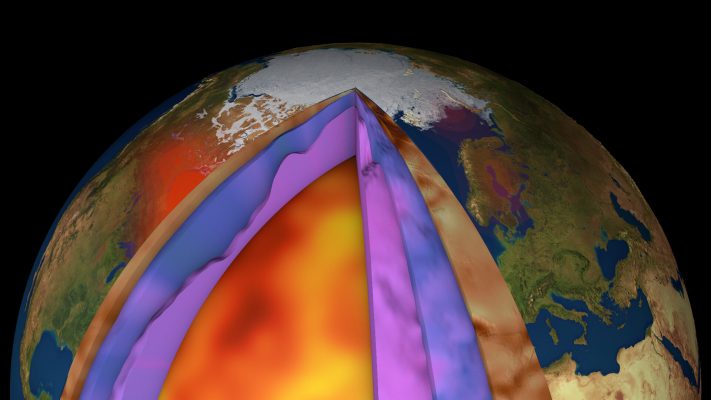
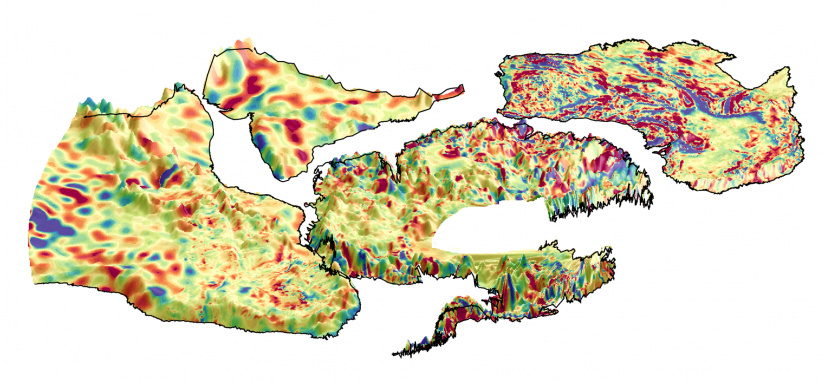
Prime company: UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS, SCHOOL OF EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT (GB)Living Planet Fellowship research project carried out by Matthew Gaddes. The Earth’s subaerial volcanoes pose a variety of threats to humanity, yet the vast majority remain unmonitored. However, with the advent of the latest synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellites, interferometric SAR (InSAR) has evolved into a tool that can be used to monitor the majority …