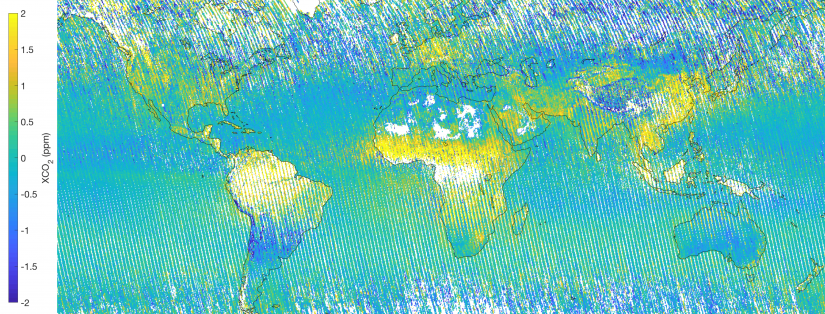
Anthropogenic CO2 emission sources detected from space
A recent study provides maps of man-made carbon dioxide anomalies around the globe. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most important anthropogenic greenhouse gas and its increase in the atmosphere is responsible for the global warming. CO2 is emitted into the atmosphere by the burning of fossil fuels. Satellite-based observations provide information on the concentration of …