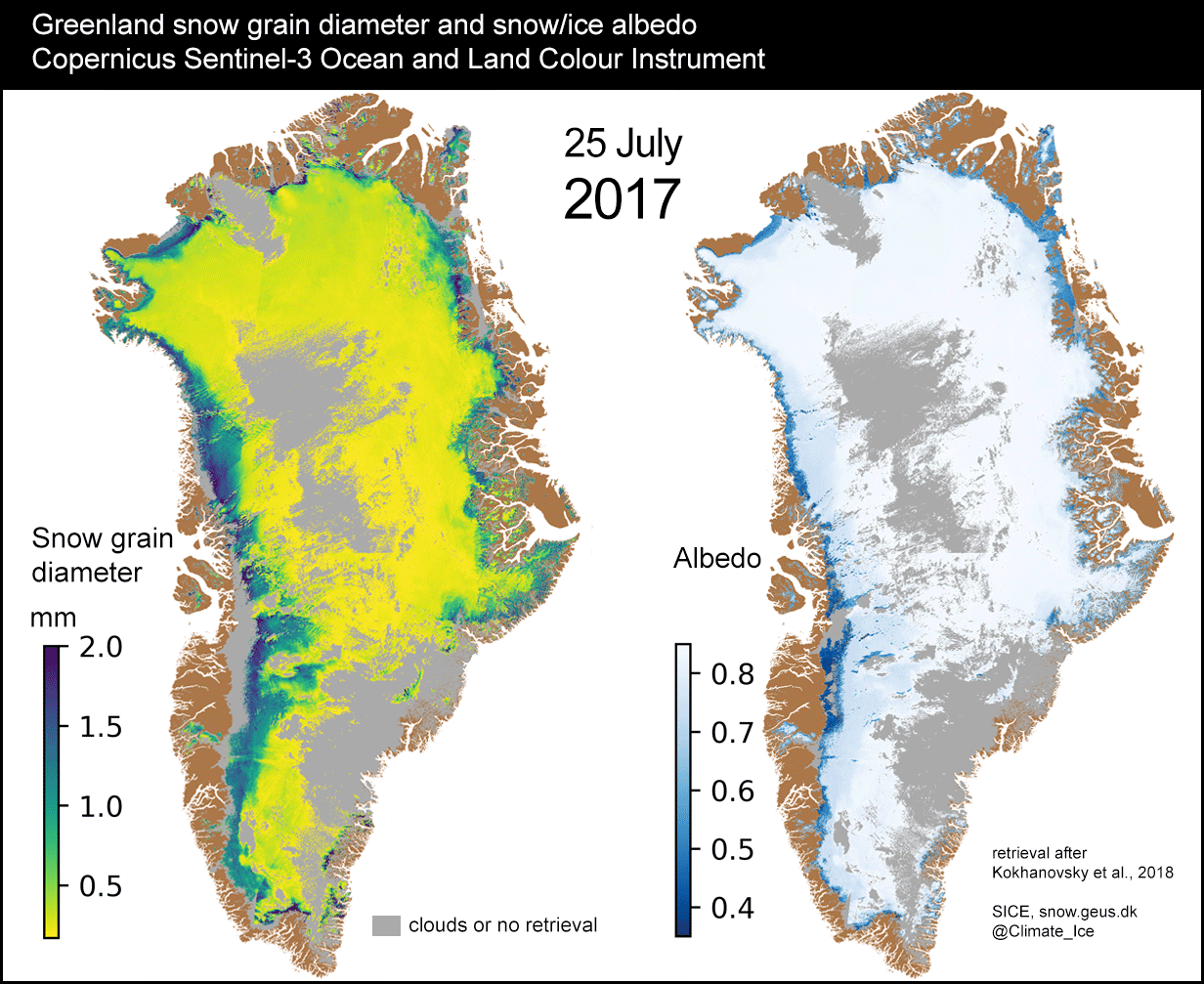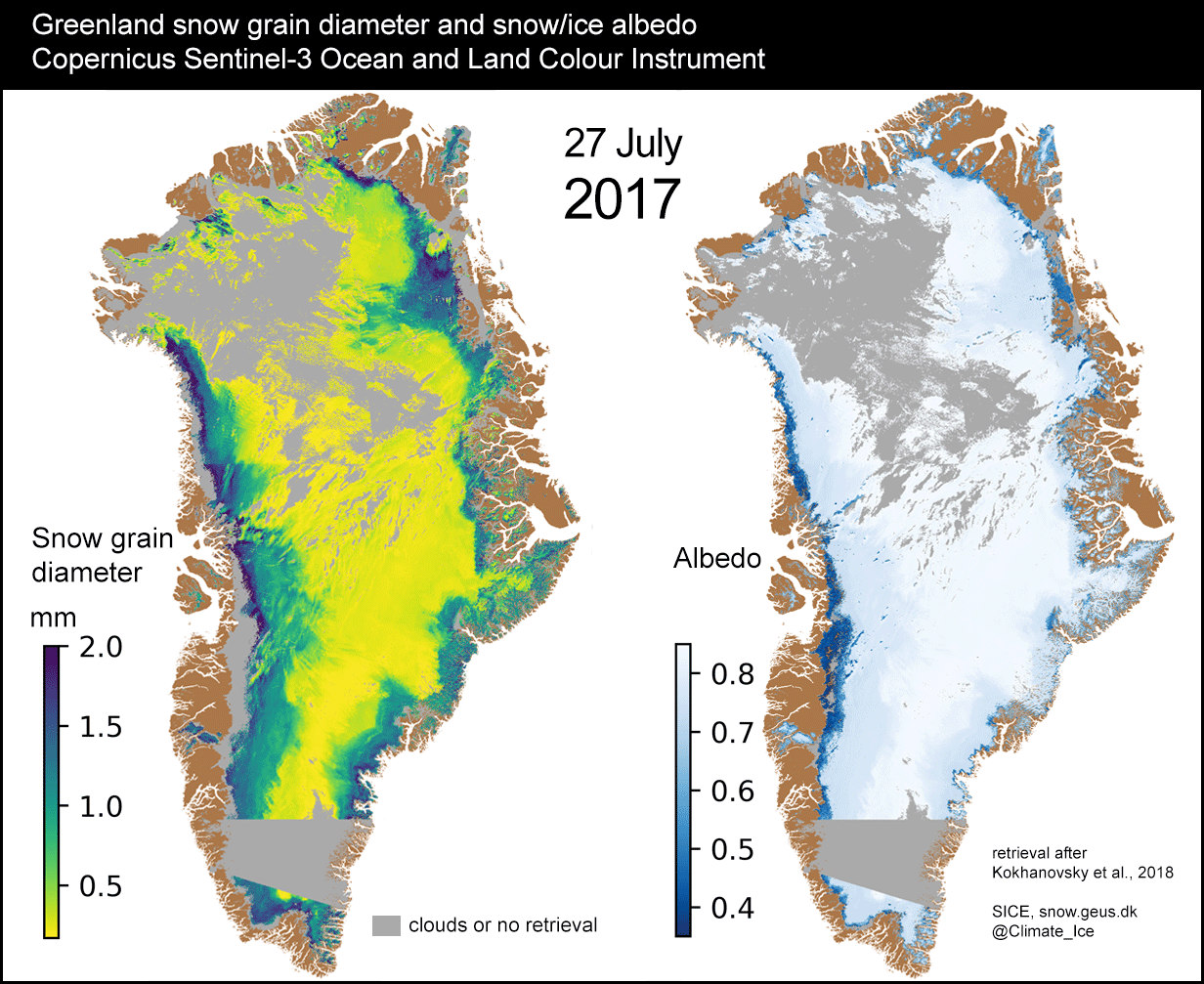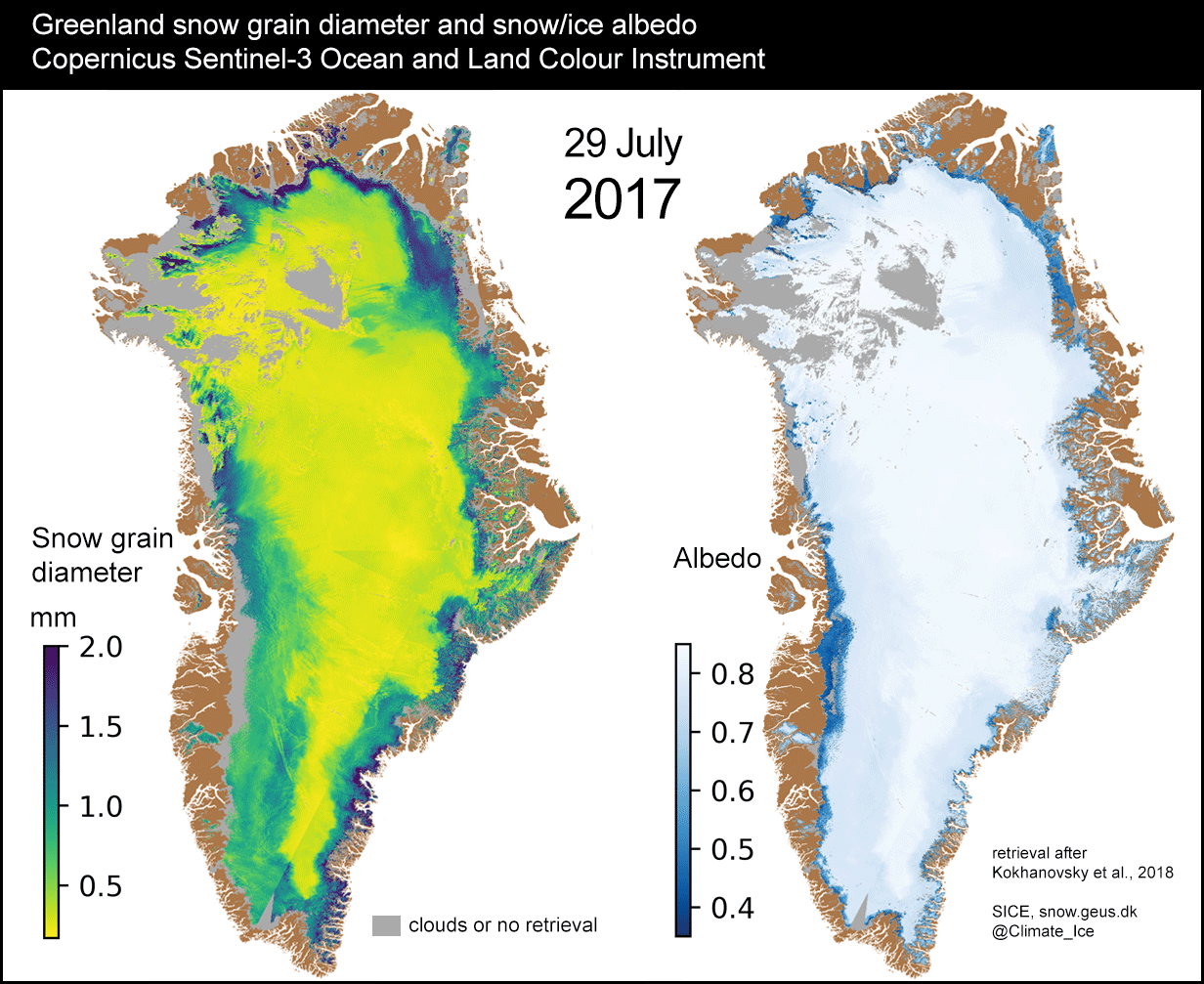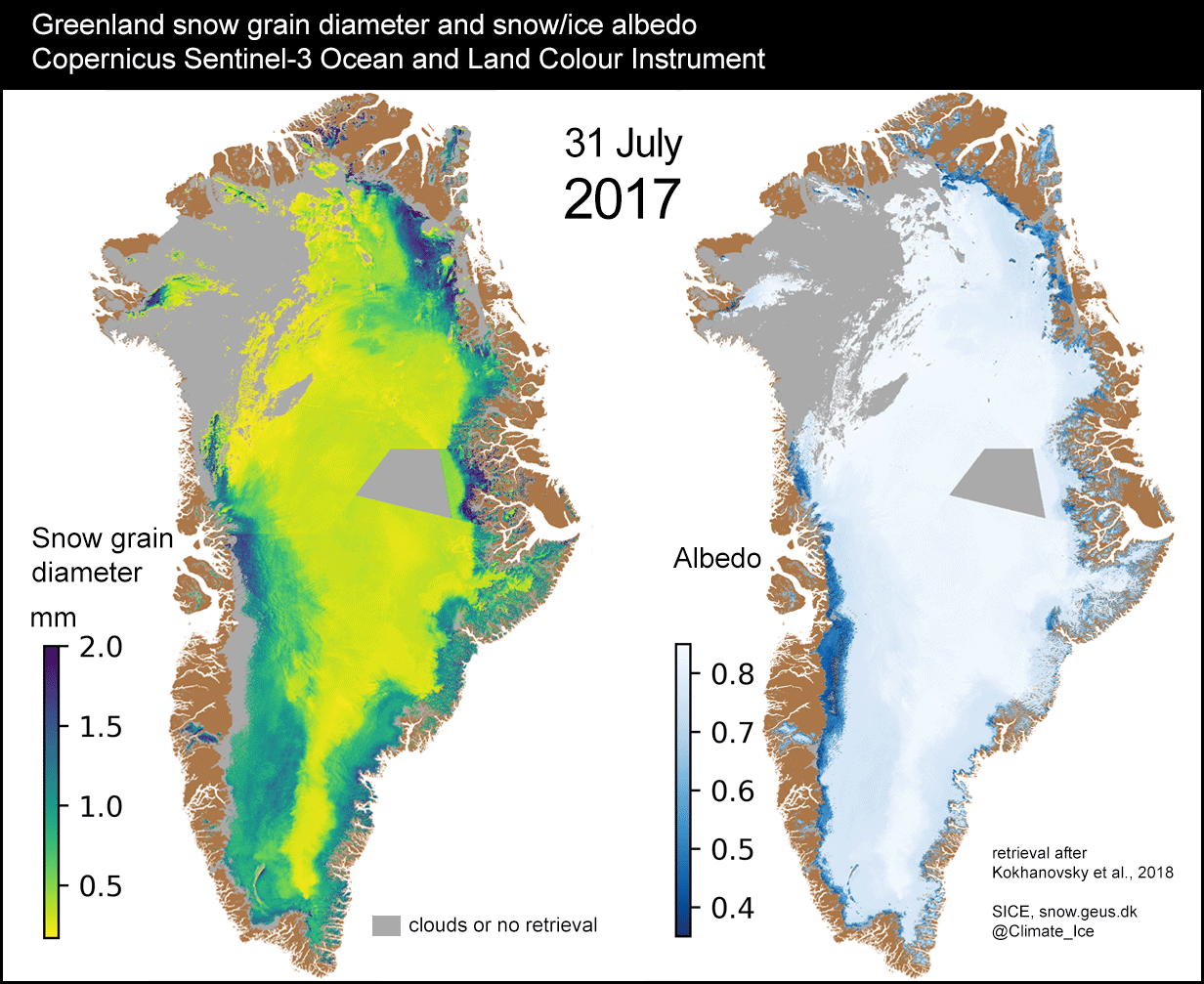
SENTINEL-3 TANDEM FOR CLIMATE (S3TC)
Prime company: ACRI-ST S.A.S. (FR)After 2 years in orbit, the Sentinel-3A satellite from the Copernicus program was joined by Sentinel-3B. During the first six months of the mission, the two satellites will fly in close formation. Sentinel-3A and Sentinel-3B observe the same place on the Earth within 30 seconds. This so-called tandem phase makes it possible to inter-calibrate very accurately the …