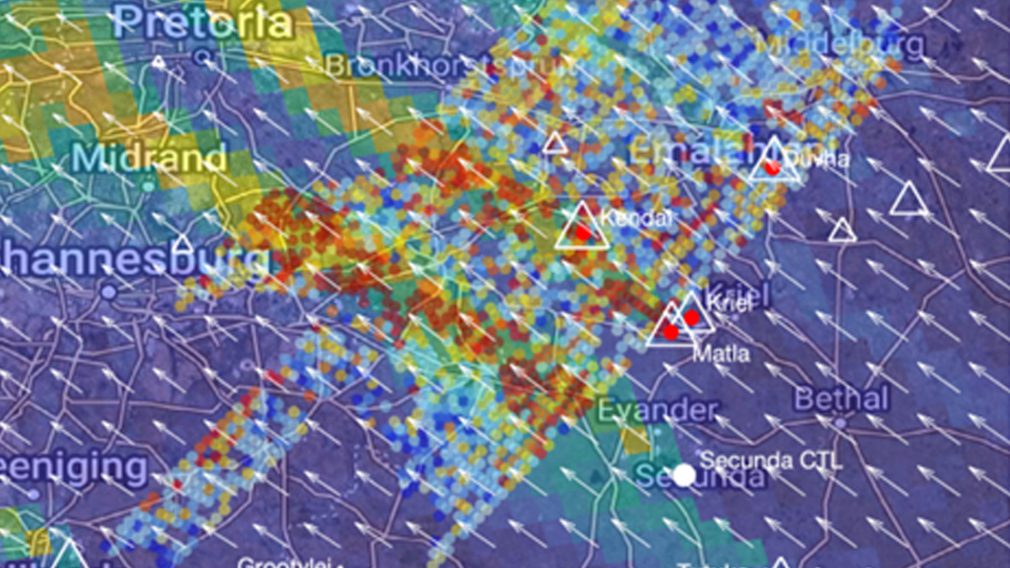
A team of researchers estimated the carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from coal-fired power plants and other major anthropogenic point sources in the South African Highveld region using space-based data. The results indicate that CO2 emissions can be obtained also in challenging cases where the plumes from multiple sources overlap.
The new publication characterizes CO2 emissions using data from NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and European Copernicus Sentinel-5P/TROPOMI.
The article analyses the emissions of six power stations (Kendal, Kriel, Matla, Majuba, Tutuka and Grootvlei) and the largest single emitter of greenhouse gas in the world, Secunda CTL synthetic fuel plant. The annual CO₂ emissions of the Secunda CTL exceed the emissions of several European countries, including Finland, Norway, and Portugal.
Overall, the space-based emission estimates are in good agreement with the emission inventories. Thus, satellite observations can be used for CO2 emission estimation and are particularly useful when no other information is available.
Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 mission operates on the International Space Station (ISS). To support the quantification and monitoring of anthropogenic CO₂ emissions, OCO-3 incorporates a new key capability that provides observations in Snapshot Area Maps (SAMs), providing contiguous images over regions as large as 80 km by 80 km in two minutes. Altogether the article analyzes six OCO-3 SAMs jointly with Sentinel-5P/TROPOMI nitrogen dioxide (NO2) columns.
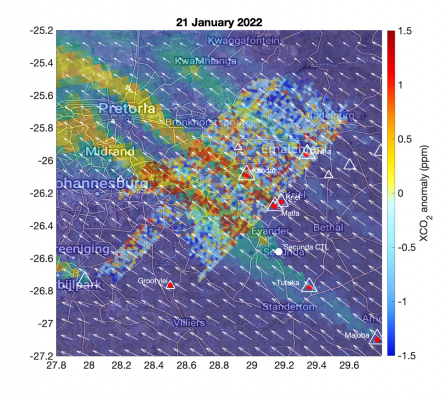
The new article is a continuation of the previous work where the authors studied the emissions and NOx-to-CO₂ emission ratio of the isolated Matimba power station. The article extends the method to challenging cases where CO₂ plumes from multiple sources overlap.
The applicability of similar emission estimation approaches for future satellite missions such as the Copernicus Carbon Dioxide Monitoring mission CO2M is discussed. CO2M is Copernicus Sentinel Expansion mission and will focus on carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere specifically through human activity.
The research was carried on in the DACES project, which focuses on detecting anthropogenic CO₂ emissions sources by exploiting the synergy between satellite-based observations of short-lived polluting gases (such as NO₂) and greenhouse gases.
The full publication by Hakkarainen and co-authors can be found at the following link: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/acb837