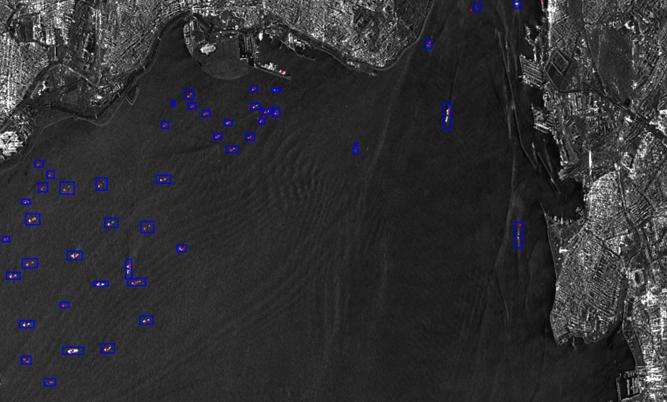
Building on the story published last February, this update highlights new advanced innovative Inverse-SAR (ISAR) algorithms developed and tailored for satellite platforms within the EO4Security ISAR project. These innovations support a wide range of use cases and represent significant progress in Earth observation for security applications.
Techniques explored
The following techniques were investigated:
- Parametric autofocus algorithms, using image contrast maximization, to remove defocusing effects due to azimuthal chirp rate mismatch, and assess motion parameters.
- Non-parametric autofocus algorithms, to remove defocusing terms, even higher than second order, from Doppler phase.
- Cross-range scaling, to estimate the azimuth real spacing thus enabling fine target’s physical dimensions retrieval.
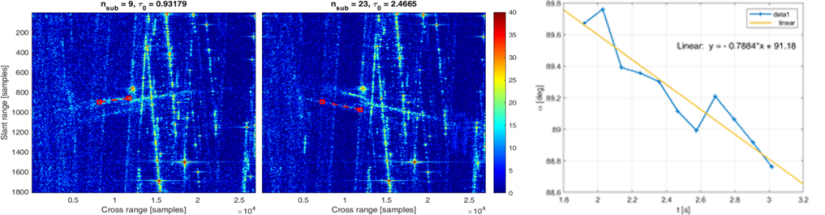
- Azimuthal sub-aperture analysis, to identify the coherent processing time intervals in which the target dynamic is enough regular to guarantee the unicity of the image projection plane (IPP).
- Non-coherent sub-apertures change detection, to detect moving targets in the challenging land domains where targets are small, fast and often under clutter conditions.
These methods were tested on a large set of VHR SAR images collected from multiple X-band VHR SAR missions, such as TerraSAR-X, PAZ, and the newer missions ICEYE, Capella Space, and UMBRA. Automatic Identification System (AIS) data were used for validation on maritime scenarios. Agreements with the satellite operators Airbus, Capella Space and Umbra, and the AIS data provider Spire supported the project activities.
Applications across domains
A variety of operational domains and target dynamics were considered:
- Maritime domain awareness. Robust capabilities in refocusing and estimating motion parameters of vessels were demonstrated. ISAR-based velocity and trajectory estimates were tested against AIS data, confirming their accuracy and operational potential for ship monitoring and classification. More advanced modes capitalizing on very long dwells also indicate the potential for enhancing target classification and revealing finer ship details.
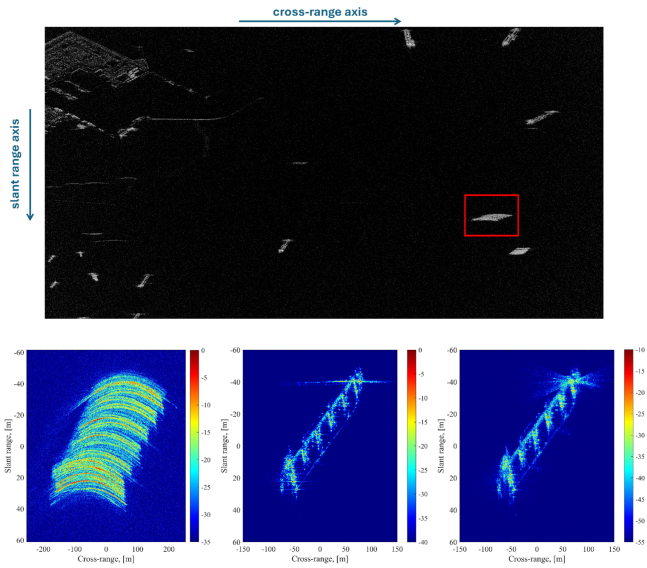
- Land domain awareness. The application of ISAR techniques for ground target detection and motion analysis in complex cluttered environments was explored. While promising, the results highlighted the need for further advancements in motion compensation to match, in very complex environments, the maturity observed in maritime scenarios.
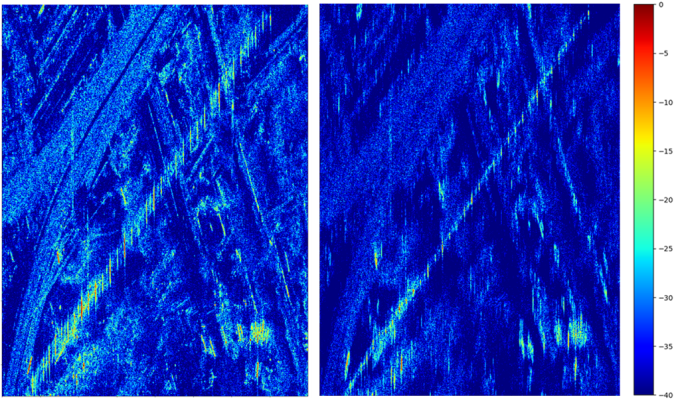
- Inland waterways monitoring. We successfully tested ISAR techniques on rivers and canals scenarios, where accurate detection and relocation of vessels was achieved without the need for external motion data.
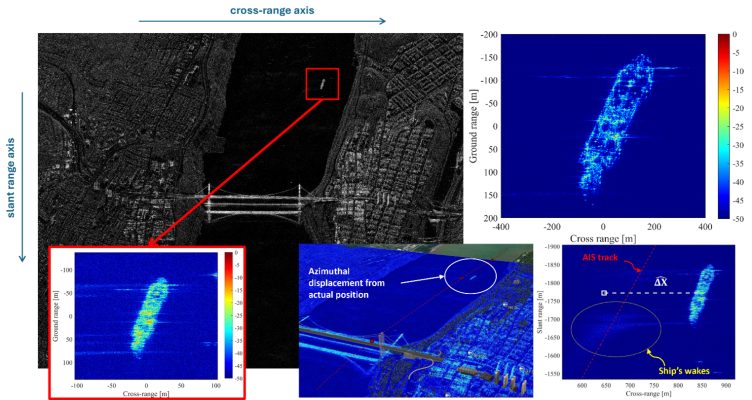
- Infrastructure monitoring. Novel ISAR processing techniques, mainly based on sub-aperture analysis, were tested for the analysis of wind turbines, including extraction of structural and rotational features. Applications to monitor the farms health status in offshore and remote environments are very interesting.
- Airport monitoring. We investigated aircraft monitoring during taxi and take-off manoeuvres. ISAR techniques improved target visibility and shape definition, demonstrating strong potential to support traffic monitoring and the classification/recognition of moving aircraft through successive ML/DL inference processing.
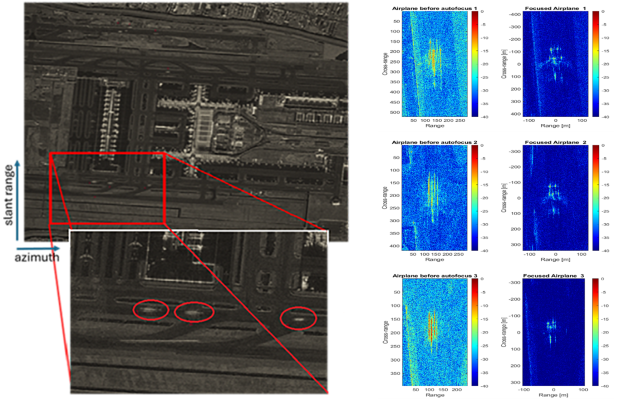
By bridging the gap between theoretical radar methodologies and real-world satellite data applications, the EO4Security-ISAR project has laid the groundwork for enhanced situational awareness services in domains where the possibility to obtain well refocused images of moving targets along with their kinematic parameters is strategic, opening the way to fine feature extraction, classification, and recognition capabilities.
Interested in learning more?
If you are interested in learning more about results from ESA’s ongoing research activities, including the submission of a patent related to micro-doppler techniques, as well as new research directions in this domain, and you are attending LPS25 in Vienna next week, don’t miss the Advanced SAR processing techniques for security and safety applications session.
This will take place on Thursday 26, 8:30 – 10:00 in Hall N1/N2.
Featured image : TerraSAR-X Spotlight Image over Mediterranean Sea area close to Bosporus Strait. Credit: Airbus Defence and Space GmbH